Scientists discover 'needle in a haystack' black hole

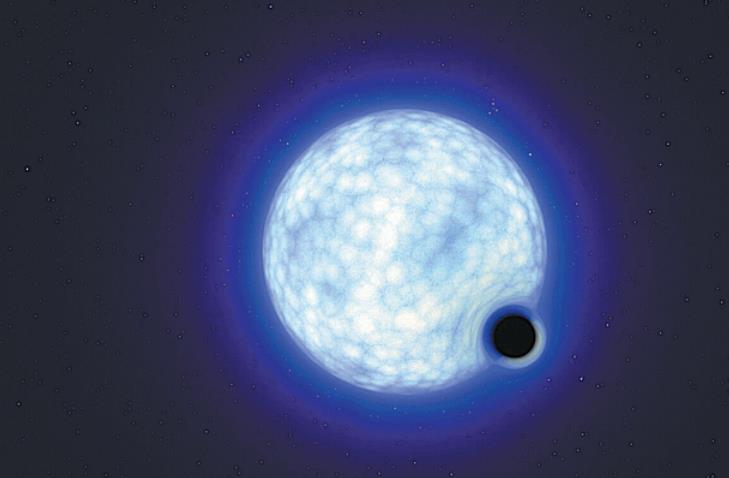
WASHINGTON-Astronomers have spotted in a galaxy adjacent to the Milky Way what they are calling a cosmic "needle in a haystack"-a black hole that not only is classified as dormant, but also appears to have been born without the explosion of a dying star.
Researchers said on Monday this one differs from all other known black holes in that it is "X-ray quiet"-not emitting powerful X-ray radiation indicative of gobbling up nearby material with its strong gravitational pull-and that it was not born in a stellar blast called a supernova.
Black holes are extraordinarily dense objects with gravity so intense that not even light can escape.
This one, with a mass at least nine times greater than the sun, was detected in the Tarantula Nebula region of the Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy and is located about 160,000 light years from Earth. A light year is the distance light travels in a year, about 5.9 trillion miles (9.5 trillion kilometers).
An extremely luminous and hot blue star with a mass about 25 times that of the sun orbits with this black hole in a stellar marriage. This so-called binary system is named VFTS 243. The researchers believe the companion star will eventually also become a black hole and could merge with the other one.
Dormant black holes, thought to be relatively common, are hard to detect because they interact very little with their surroundings. Numerous prior proposed candidates have been debunked with further study, including by members of the team that uncovered this one.
"The challenge is finding those objects," said Tomer Shenar, a research fellow in astronomy at the University of Amsterdam, and lead author of the study published in the journal Nature Astronomy. "We identified a needle in a haystack."
"It's the first object of its kind discovered after astronomers have been searching for decades," said astronomer and study co-author Kareem El-Badry of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics.
The researchers used six years of observations from the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope in Chile.
There are many different categories of black holes. The smallest, like the newly detected one, are so-called stellar mass black holes formed by the collapse of massive individual stars at the end of their life cycles. There are also intermediate mass black holes as well as the enormous supermassive black holes residing at the center of most galaxies.
"Black holes are intrinsically dark objects. They do not emit any light. Therefore, in order to detect a black hole, we usually look at binary systems in which we see one luminous star moving around a second, not-detected object," said study co-author Julia Bodensteiner, a postdoctoral research fellow at the European Southern Observatory in Munich, Germany.
It is typically assumed that the collapse of massive stars into black holes is associated with a powerful supernova explosion. In this case, a star perhaps 20 times the sun's mass blew some of its material into space in its death throes, then collapsed in on itself without an explosion.
The shape of its orbit with its companion offers evidence for the lack of an explosion.
"The orbit of the system is almost perfectly circular," Shenar said.
Had a supernova occurred, the blast's force would have kicked the newly formed black hole in a random direction and yielded an elliptical rather than circular orbit, Shenar added.
Black holes can be mercilessly ravenous, guzzling any material-gas, dust and stars-wandering within their gravitational pull.
"Black holes can only be mercilessly ravenous if there is something close enough to them that they can devour. Usually, we detect them if they are receiving material from a companion star, a process we call accretion," Bodensteiner said.
Shenar said: "In so-called dormant black hole systems, the companion is far enough away that the material does not accumulate around the black hole to heat up and emit X-rays. Instead, it is immediately swallowed by the black hole."
Xinhua - Agencies

































